Psychiatric nurse practitioners vs psychiatrists: how mental health nurse practitioners are filling gaps in healthcare.
America faces a broad range of mental health issues from opioid addiction to increasing rates of depression and suicide. One in every five Americans has suffered or will suffer from mental illness, yet the number of psychiatrists in the country is dwindling. Over 75% of U.S. counties have a shortage of mental health prescribers. The demand for psychiatric mental health nurse practitioners is increasing because they have the scope of practice needed fill this gap in care.
There are several factors that contribute to the demand for psychiatric nurse practitioners:
- There is a psychiatrist shortage stemming from an aging profession. According to American Association of Medical Colleges, more than 60% of psychiatrist are over the age of 55.
- Millions lack access to quality mental health care. The Affordable Care Act reduced cost and enhanced availability for mental health care, which affirmed the existing shortage leaving people struggling to find appropriate resources.
- Little to no mental health professionals exist in rural areas. In addition to the overall shortage of physicians in rural areas, over 60% of rural Americans reside in designated mental health provider shortage areas.
- Society destigmatizes mental illnesses. Negative connotations surrounding mental health have historically kept many individuals from seeking treatment. The de-stigmatization of mental illness in mainstream media/society has made the topic more easily addressable and has further increased the demand for individuals to seek qualified mental health professionals, reiterating the obstacles between patients and the treatment they need.
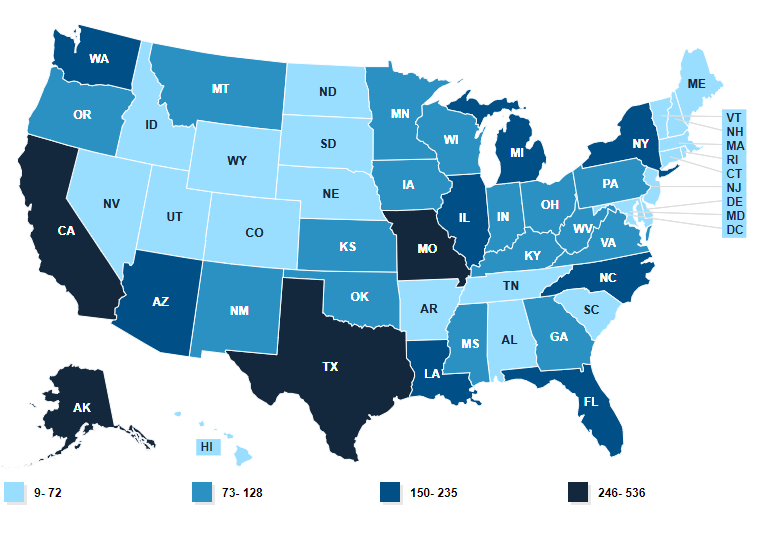
The map below ranks the availability of the mental health workforce in the US. States with the lowest number of shortage areas are in light blue, and the states with the highest number of shortage areas (lowest access to care) are in dark blue.
Why NPs?
Nurse practitioners bring a different perspective by virtue of their training. Mental health patients need a lot of support and interaction and NPs bring unique qualities that can be useful in treating a patient of this sort. Nurse practitioners take a more holistic approach to treating patients, one that is both individualized and hands-on. Patients seeing nurse practitioners tend to have higher levels of satisfaction with their care. Nurse practitioners cost less than psychiatrists but deliver the same level of efficiency, and are more likely to practice in rural areas. Psychiatric nurse practitioners can help satisfy the demand for psychiatrists and contribute to the overall mental health of the country.







